Can I Drink Water Bottle Left in Car? A Comprehensive Guide
You shouldn’t drink water from a plastic bottle left in a hot car. Heat causes chemicals like Bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates to leach into the water, posing health risks such as reproductive issues and certain cancers.
Warm temperatures also promote bacterial growth, which could lead to gastrointestinal infections. Even BPA-free plastics can contain other harmful substances that leach into water under heat exposure.
To stay safe, store bottles in cool, shaded areas and consider using metal or glass containers. By understanding these risks, you can make better decisions about your drinking water.

Key Takeaways
- High temperatures in cars cause plastic bottles to leach harmful chemicals like BPA into the water.
- Warm car environments promote bacterial growth, increasing the risk of gastrointestinal infections.
- Avoid drinking water stored in cars during hot weather to prevent chemical and bacterial contamination.
- Use insulated containers and store water in cool, shaded areas to maintain safety.
Chemical Leaching Risks
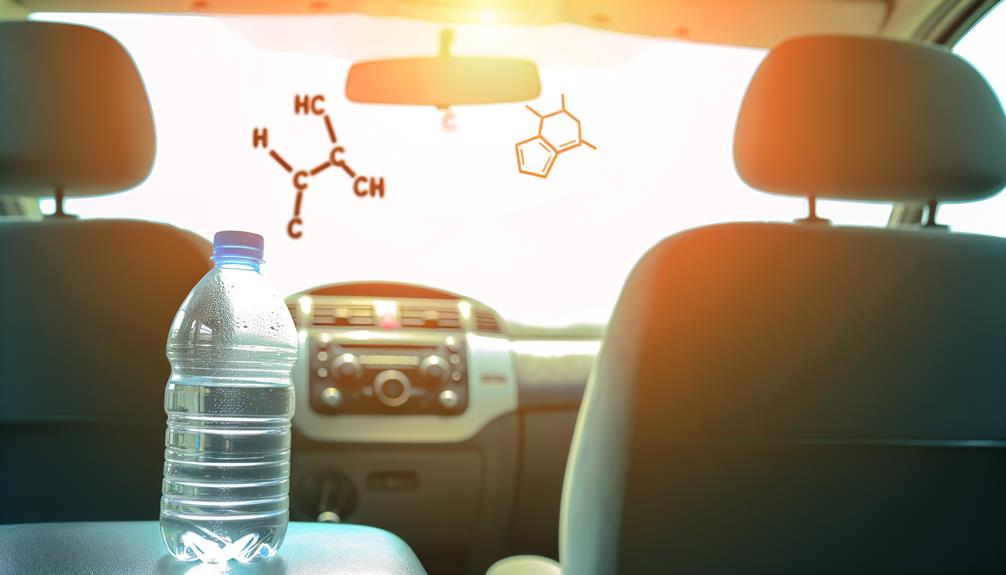

When water is left in a car, the heat can cause chemicals from the plastic bottle to leach into the water, posing potential health risks.
Studies have shown that substances like Bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates can migrate from plastic into water. These chemicals are known endocrine disruptors, meaning they can interfere with hormone systems in your body.
Research indicates that long-term exposure to these compounds may contribute to health issues such as reproductive problems, metabolic disorders, and even certain cancers.
You should be cautious about consuming water from bottles that have been exposed to high temperatures. Ensuring your bottled water is stored in a cool, shaded place can help mitigate these risks, protecting your health in the long run.
Temperature Effects on Plastic
High temperatures can accelerate the degradation of plastic, leading to increased leaching of harmful chemicals into the water.
When you leave a water bottle in a hot car, the elevated temperature can cause the plastic to break down faster.
Studies have shown that chemicals like BPA and phthalates, commonly found in many plastics, may seep into the water more readily under heat.
The higher the temperature, the greater the risk of these chemicals contaminating your drink.
Even if a bottle is labeled BPA-free, other potentially harmful substances could still leach out.
As a result, it’s essential to reflect on the impact of heat on plastic and its potential health risks when deciding whether to drink water left in your car.
Bacterial Growth Concerns

Bacterial growth in water left in a car can pose significant health risks, as warm temperatures create an ideal environment for microbes to proliferate. When the temperature inside your car rises, it accelerates the rate at which bacteria multiply in the water bottle.
Research indicates that bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella thrive in these conditions. Even if the water appears clear, it can harbor these invisible pathogens.
Using a sealed bottle might reduce contamination, but it doesn’t eliminate the risk entirely. Studies have shown that plastic surfaces can still harbor bacteria, leading to potential contamination of the water inside.
Monitoring the time and temperature exposure of your water bottle is essential to minimizing bacterial growth and ensuring safety.
Health Implications
Leaving water in your car can lead to bacterial growth, especially if the bottle has been opened.
Additionally, heat can cause chemicals from the plastic to leach into the water, posing potential health risks.
Understanding these factors is essential for making informed decisions about drinking water left in your vehicle.
Bacterial Growth Concerns
When water sits in a warm car for extended periods, the heat creates an ideal environment for bacterial growth, posing potential health risks. Bacteria thrive in warm, moist environments, making your water bottle a potential breeding ground.
Research indicates that consuming water from a contaminated bottle can lead to various health issues, including:
- Gastrointestinal infections: Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Food poisoning: Caused by bacteria like E. coli and Salmonella.
- Skin infections: If the water contacts skin wounds or abrasions.
You should be particularly cautious if the bottle has been opened, as this increases the likelihood of bacterial contamination.
Always prioritize your health by opting for fresh, uncontaminated water.
Chemical Contamination Risks
Exposure to heat can cause chemicals like BPA and phthalates to leach from plastic water bottles, posing significant health risks.
Studies show that when plastic bottles are left in hot environments, such as a car, these chemicals can migrate into the water. BPA is known to disrupt endocrine function, which can lead to hormonal imbalances and potentially increase cancer risk.
Phthalates, on the other hand, are linked to reproductive issues and developmental problems. You should be cautious about consuming water that’s been stored in a heated vehicle.
Opt for bottles made from safer materials like stainless steel or glass, which don’t leach harmful substances when exposed to high temperatures. This simple switch can help you avoid these chemical contamination risks.
Safe Storage Practices
Storing water in a cool, shaded location greatly reduces the risk of chemical contamination from the plastic bottle. High temperatures can accelerate the leaching of harmful chemicals like BPA and phthalates into the water.
To guarantee safety, follow these guidelines:
- Store bottles indoors: Keep them in a pantry or cupboard, away from direct sunlight.
- Avoid car storage: Cars can reach extreme temperatures, making them unsuitable for water storage.
- Use insulated containers: These help maintain a stable, cool temperature for longer periods.
Alternatives to Plastic Bottles
Switching to reusable metal containers or glass water bottles can greatly reduce your exposure to harmful chemicals like BPA and phthalates, which are often found in plastic.
Studies show that these alternatives aren’t only safer but also more environmentally sustainable.
Reusable Metal Containers
Many people are now opting for reusable metal containers as a safer and more environmentally-friendly alternative to plastic bottles. Scientific studies highlight several advantages:
- Durability: Metal containers, particularly stainless steel, resist wear and tear, making them long-lasting.
- Thermal Insulation: They often come with insulation properties, keeping your drinks hot or cold longer.
- Non-Toxic: Unlike some plastics, metals like stainless steel don’t leach harmful chemicals into your water.
When choosing a reusable metal container, you’re making a scientifically-backed decision that benefits both your health and the planet.
Studies confirm that these containers maintain water quality better than plastic, especially when exposed to varying temperatures in your car.
Glass Water Bottles
Glass water bottles offer a clean, non-toxic alternative to plastic bottles, providing a safe way to store and transport your drinking water. Unlike plastic, glass doesn’t leach harmful chemicals like BPA or phthalates, even when exposed to high temperatures.
Studies confirm that glass maintains the purity and taste of water, free from contamination. It’s also highly durable and recyclable, reducing environmental impact.
However, you must handle glass with care to avoid breakage. If left in a hot car, glass bottles are less likely to degrade or release toxins compared to plastic.
Their resilience to chemical reactions makes them a safer choice for your hydration needs, contributing to both personal health and environmental sustainability.
Expert Opinions

Several experts in environmental health and food safety agree that the safety of drinking water left in a car depends on various factors, including temperature and duration. They emphasize that high temperatures can lead to the release of harmful chemicals from plastic bottles into the water. Additionally, prolonged exposure can increase the chances of bacterial growth.
Here’s what you should consider:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate chemical leaching and bacterial growth.
- Duration: The longer water sits in a heated environment, the greater the risk.
- Bottle Material: Plastics, especially those containing BPA, are more prone to chemical release.
Understanding these factors helps you make informed decisions about drinking water left in your car.
Final Recommendations
To guarantee your safety, avoid drinking water that’s been left in a car for extended periods, especially in high temperatures.
Studies have shown that prolonged heat exposure can cause chemicals like BPA and phthalates to leach from plastic bottles into the water. These chemicals have been linked to various health risks, including endocrine disruption and potential carcinogenic effects.
Additionally, stagnant water in a warm environment can become a breeding ground for bacteria, posing further health risks.
For ideal safety, store water in stainless steel bottles and keep them in cool, shaded areas when not in use. If you must leave water in your car, make sure it’s for a short duration and avoid high-temperature conditions.
Prioritize your health by adopting these precautions.
Conclusion
Coincidentally, the risks of drinking water from a bottle left in your car align with several health concerns. On hot days, the heat can cause chemicals from the plastic bottle to leach into the water, potentially leading to health risks. Additionally, repeated use of the same bottle without proper cleaning can result in bacterial growth, similar to the Brita water bottle drinking issue some users report due to inadequate maintenance. Staying mindful of these concerns can help ensure safer hydration choices.
Chemical leaching, temperature effects on plastic, and bacterial growth all pose significant threats.
It’s clear that safe storage practices and alternatives to plastic bottles are essential.
Experts agree on the potential dangers, so prioritizing your health by avoiding this habit is wise.
Remember, a little precaution today can prevent bigger health issues tomorrow.